Explain the Different Steps of Krebs Cycle
The major energy provider of the cell. Coenzyme A is released so that it can bring another molecule of acetate to the Krebs Cycle.
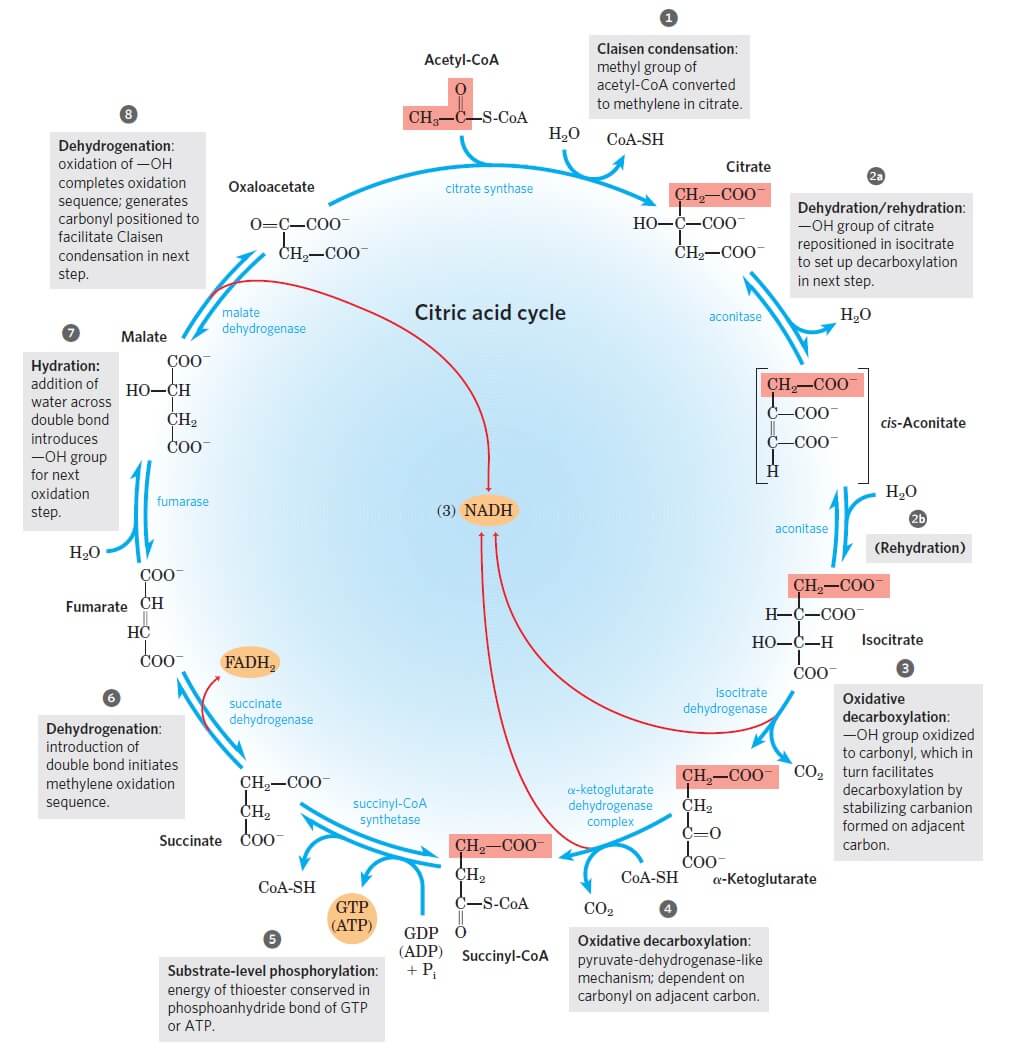
Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Tca Cycle With Steps And Diagram
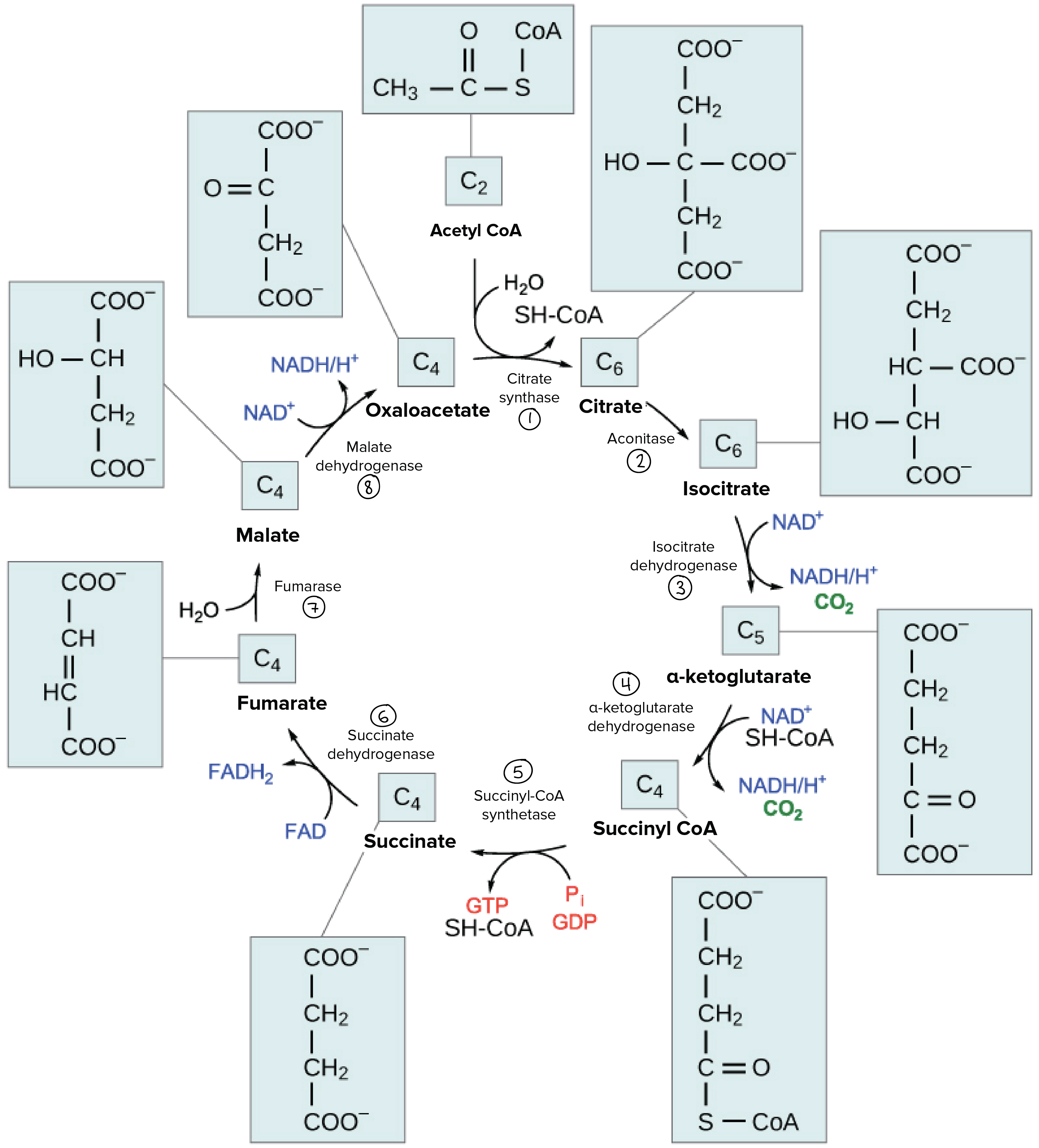
In the second step citrate gets converted to isocitrate an isomer of citrate.
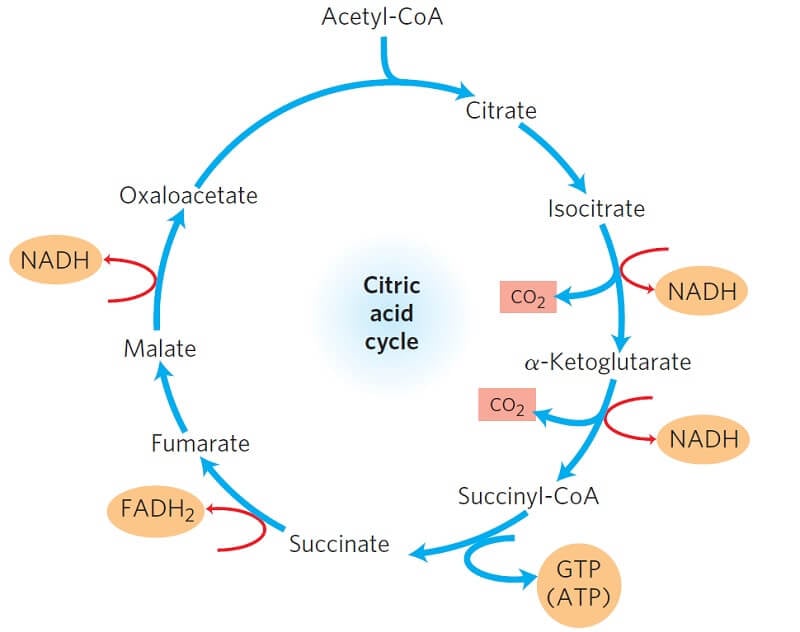
. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. So for every 1 pyruvate molecule added the Krebs cycle will produce. A dehydration-hydration sequence is used to isomerize citrate yielding 2R3S-isocitrate.
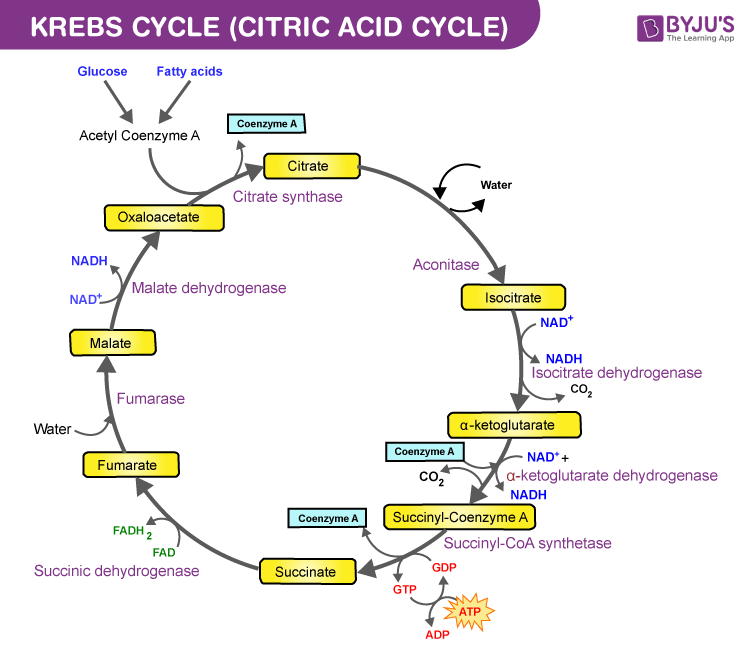
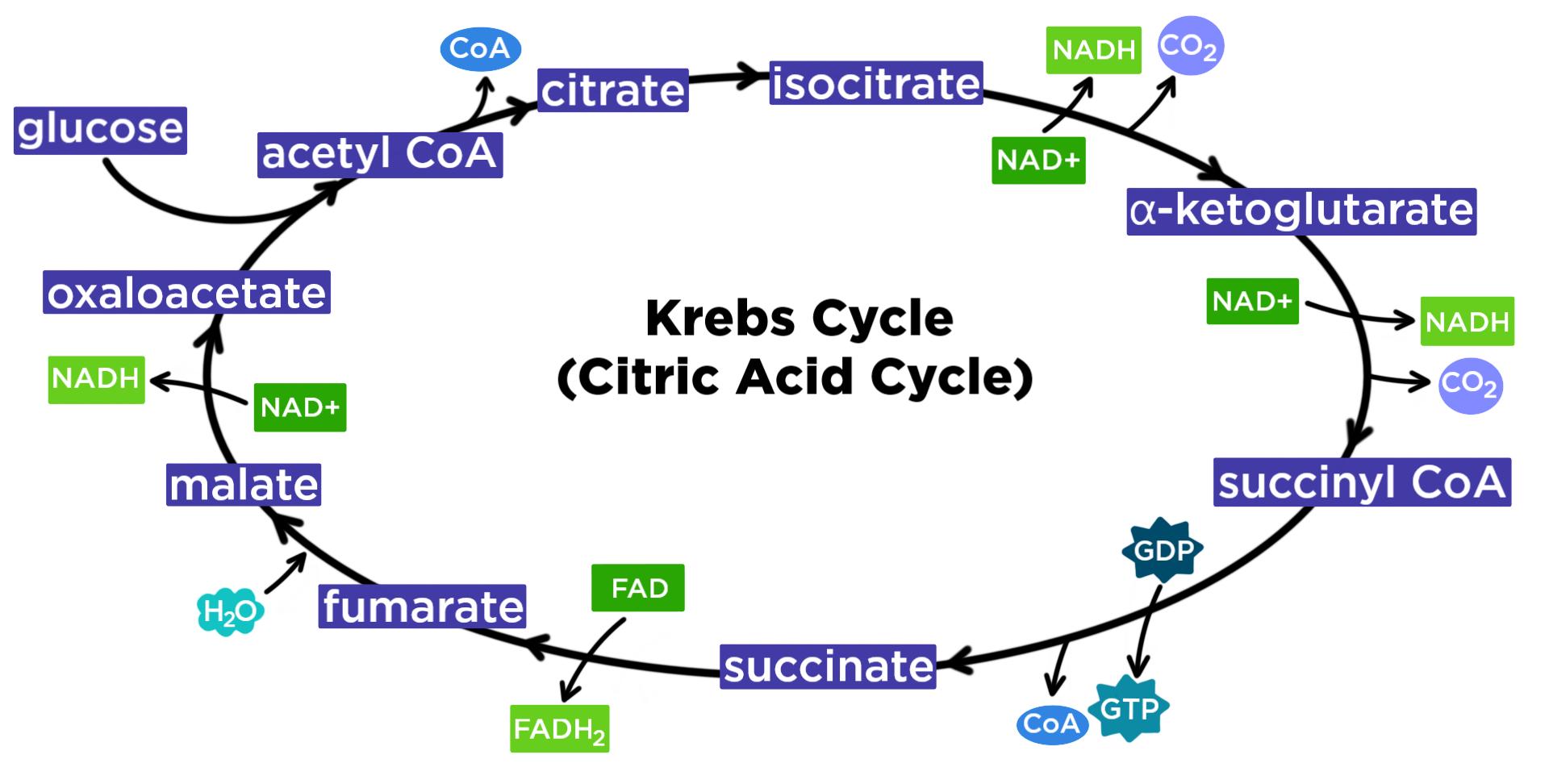
How can ATP be used to lower the body tempgive a specific example 5. Where acetate enters the Krebs Cycle 2. Acetyl CoA two carbon molecule joins with oxaloacetate 4 carbon molecule to form citrate 6 carbon molecule.
It takes place over eight different steps. Isocitrate is oxidised to alpha-ketoglutarate a five carbon. An enzyme combines the 2-carbon acetate molecules with a 4-carbon acid called oxaloacetate to form a 6-carbon acid called citrate 3.
Steps involved in Krebs cycle. 2 the high energy electrons stored within the eight NADH molecules generated will used later to. The first step is a condensation step combining the two-carbon acetyl group from acetyl CoA with a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon molecule of citrate.
List the steps of the Krebs cycle and the products it creates. The TCA cycle starts with an enzymatic aldol addition reaction of acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate which results in the. Regulation of Krebs-TCA cycle.
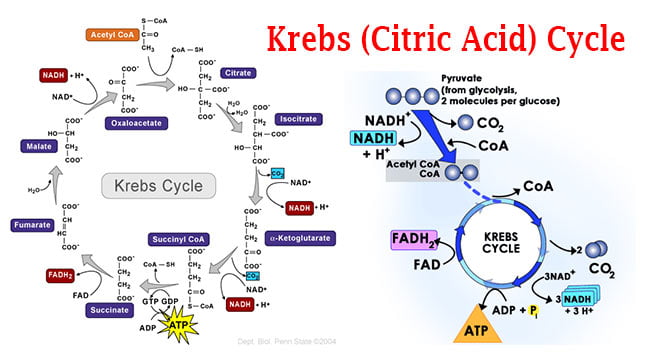
How many glucose molecules can undergo cellular respiration when 13 O2 molecules are available to react. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. NAD gets reduced to NADH.
The reaction takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. This is a two-step process. The FADH 2 and NADH generated in the Krebs cycle donate their electrons to oxygen through various electron carriers via the electron transport chain in a process known as oxidative phosphorylation.
When is carbon dioxide released during cellular respiration. Condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate.
3 molecules of NADH. 1 molecule of FADH 2. Citrate is converted to its isocitrate an an isomer of citrate by the removal of one water molecule and adding the another.
Steps of Krebs Cycle. Acetyl CoA a 2-carbon molecule combines with oxaloacetate a 4-carbon molecule. A conitase 3.
With the help of the succinate dehydrogenase enzyme the succinate is oxidised. Both processes produce ATP from substrates but the Krebs cycle produces many more ATP molecules than glycolysis. The first step is to put energy into the system.
This cycle describes a. This step is irreversible because it is highly exergonic. 2 molecules of CO 2.
During the steps of the cycle two molecules of CO 2 are released in addition to 3 more molecules of NADH one of FADH 2 and one of GTP. Its purpose is to collect high-energy electrons for use in the electron transport chain reactions. Oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
Regulation of oxidative phosphorylation. In aerobic respiration both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are involved whereas in anaerobic respiration only glycolysis takes place. Combining the Acetyl-Coa 2-carbon molecule and Oxaloacetate 4-carbon molecule to form a Citrate 6-carbon molecule.
The Krebs cycle involves converting this acetyl CoA into carbon dioxide. Use attached photo to understand easily. Citrate is converted to isocitrate an isomer of citrate Step 3.
Citrate synthatase to put energy into system 2. The combination forms the six carbon acid called citric acid as the first product is citric acid so the krebs cycle is also called as citric acid cycle. In the second step citrate is converted into its isomer isocitrate.
Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. The steps of the Krebs cycle are as follows. Citrate is produced in this step when Acetyl CoA adds its two-carbon acetyl group to oxaloacetate.
1 the decarboxylation of pyruvate represents the first of six decarboxylations within this reaction cycle one for each of the six carbon atoms present in the initial substrate glucose facilitating its complete oxidation. The various enzymes involved in different steps are. Every stage in each process is catalysed by a specific enzyme.
Citrate first loses a water molecule and then gains one to form isocitrate. The Krebs cycle also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic cycle is the first step of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells. The Krebs Cycle is the second process in the mechanism of cellular respiration which is responsible for degrading the pyruvic acid which is formed in the first step of glycolysis and forms the inorganic compounds like carbon dioxide and water aerobically in the cells mitochondria.
The Krebs cycle is simply another name for the Citric Acid Cycle so named for the researcher who identified the complete cycle in 1937. Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. The third step involves oxidation of isocitrate.
There are two things to note from this initial step of the Krebs cycle. A molecule of carbon dioxide is released leaving behind a five-carbon molecule ɑ-ketoglutarate. Purpose of this cycle is to generate electron carriers or reduction carriers.
The steps in the Krebs cycle are. 1 molecule of GTP. These carriers transfer that energy to oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
Formation of a 6-carbon molecule. CoA is bound to a sulfhydryl group -SH and diffuses away to. The Krebs cycle is known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle as well.

The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
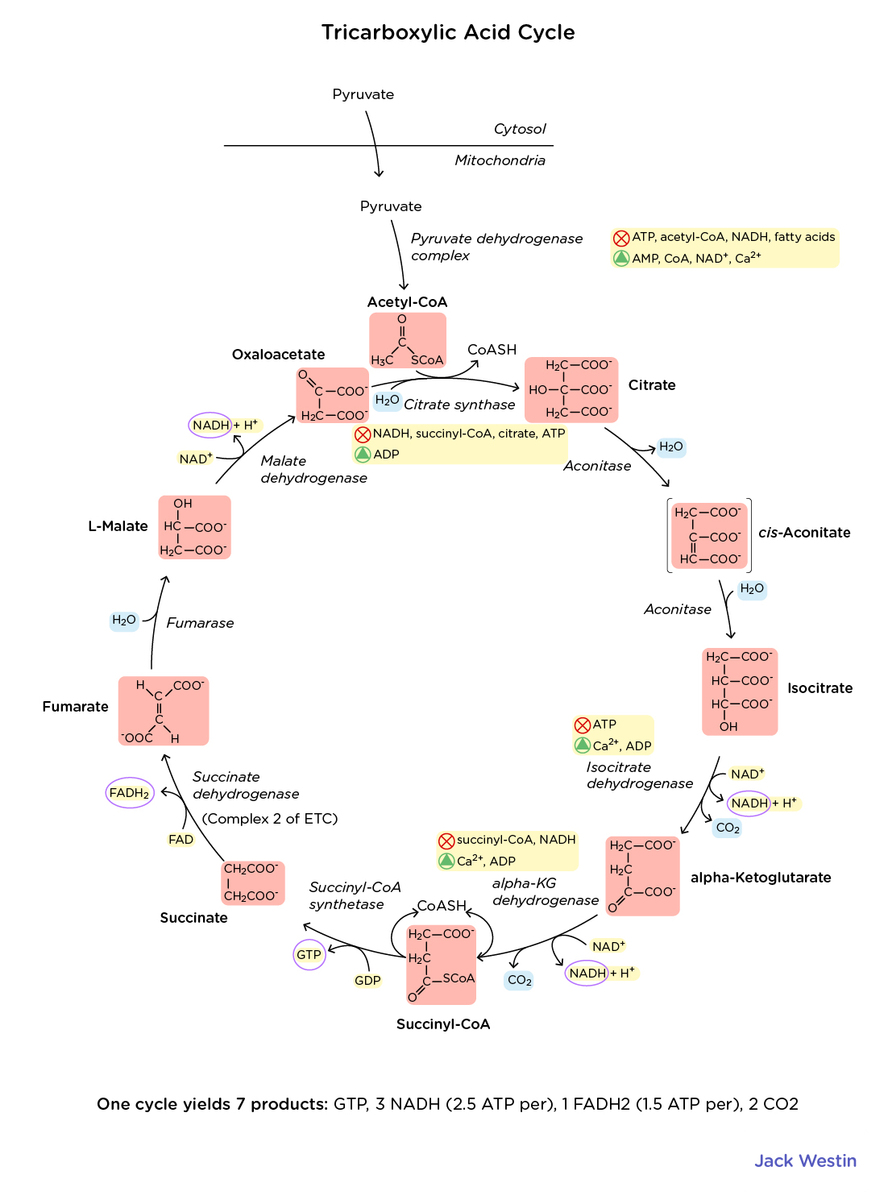
Reactions Of The Cycle Substrates And Products Citric Acid Cycle Mcat Content
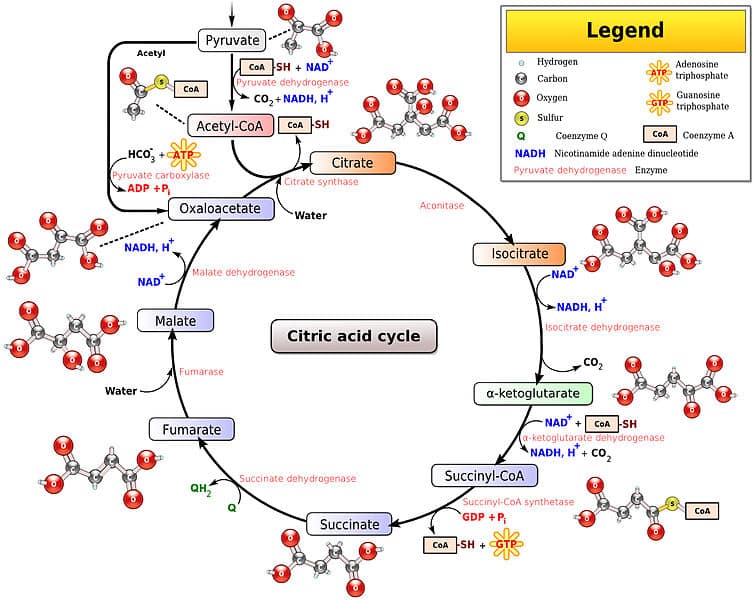
The Tca Cycle Steps Krebs Cycle Teachmephysiology

Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Tca Cycle With Steps And Diagram

Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Biochemistry Britannica
Krebs Cycle Overview Wyzant Lessons

8 Steps Of Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes And Step Wise Reaction Simplified 8 Min Part Ii Youtube
Krebs Cycle Cellular Respiration

Citric Acid Cycle And Nad Dependent Idh Action A The Download Scientific Diagram

Learn About Steps In Citric Acid Cycle Chegg Com

Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Tca Cycle With Steps And Diagram

Krebs Cycle Or Citric Acid Cycle Or Tca Cycle Online Science Notes
Krebs Cycle Or Citric Acid Cycle Steps Products Significance
The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
Krebs Citric Acid Cycle Steps By Steps Explanation Microbiology Info Com


Comments
Post a Comment